Introduction
Atomic force
microscopy or AFM is similar to STM relies on a very sharp tip, but in this
case, the tip is brought close enough to the surface that the intermolecular
forces between tip and the surface can
be measured. It is a method to see a surface in its full, three-dimensional
picture, down to the nanometer scale. This method applies to hard and soft
synthetic materials as well as biological structures (tissues, cells,
biomolecules), irrespective of opaqueness or conductivity.
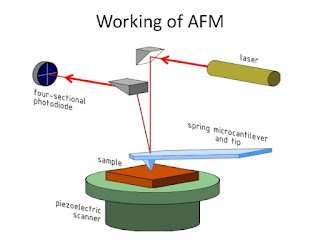
Fig: Schematic diagram of AFM instrument
Dynamiic AFM
Here cantilever driven near resonance. The cantilever's resonant
frequency, phase and
amplitude are affected by short-scale force gradients. Non-contact AFM, Tapping mode AFM,
Amplitude, Modulated AFM, Frequency
Modulated AFM are all dynamic AFM.
Conclusion
AFM
is a versatile tool to investigate
·
topography of surfaces
·
properties of surfaces
·
properties of single molecules
·
forces within molecules
But
it always consider experimental conditions and artefacts on measurements
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You ☺️